Specialist in Ice and Heat Therapy
Flex-Ice products are sold by 1000’s of Physiotherapists, Chiropractors & Osteopaths across Australia.
Email your postcode to contact@flexice.com
to find an outlet near you.
Flex-Ice
GPO Box 1079
Melbourne 3001
Australia
Ph: 03 9311 4011
Fax: 03 9311 4033
Wholesale Orders: info@flexice.com
Hospital remittance: accounts@flexice.com
International Orders: fob@flexice.com
Send Us A Message
Instructions
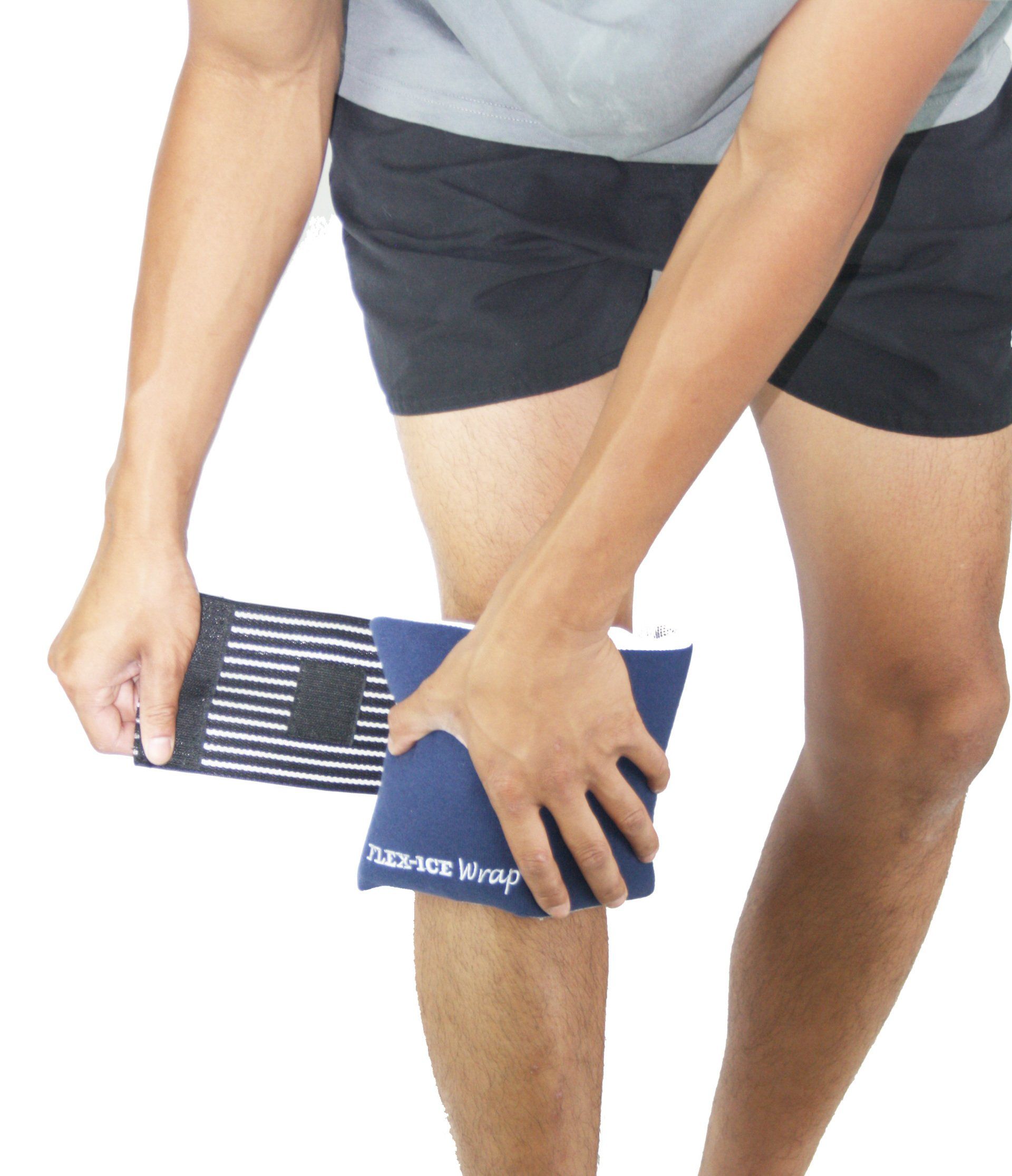
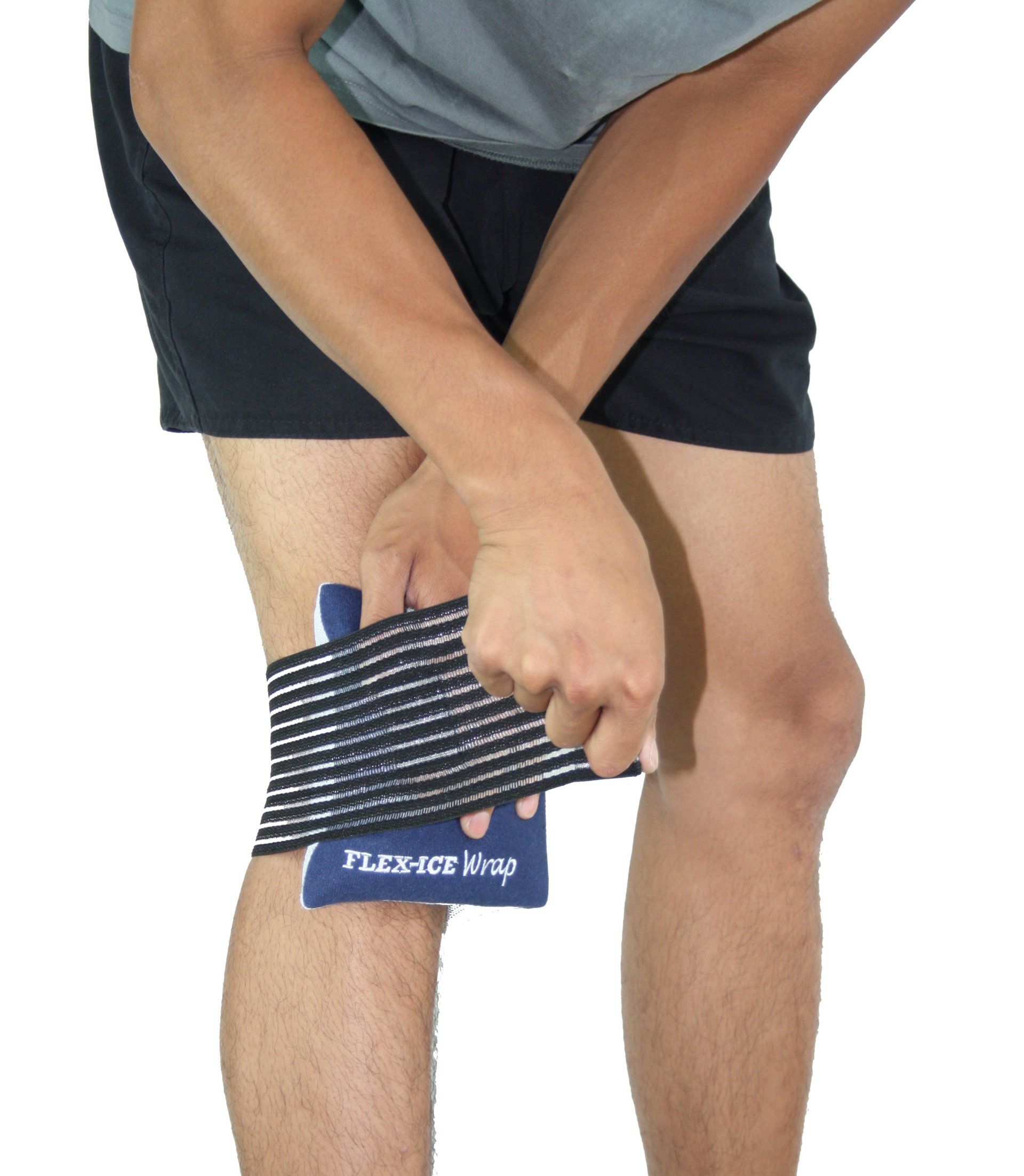
How to apply Flex-Ice Wrap
Simply insert a previously cooled or heated Flex-Ice gel pack in the pocket.

Place on the area to be treated and tighten the elastic to your desired compression.
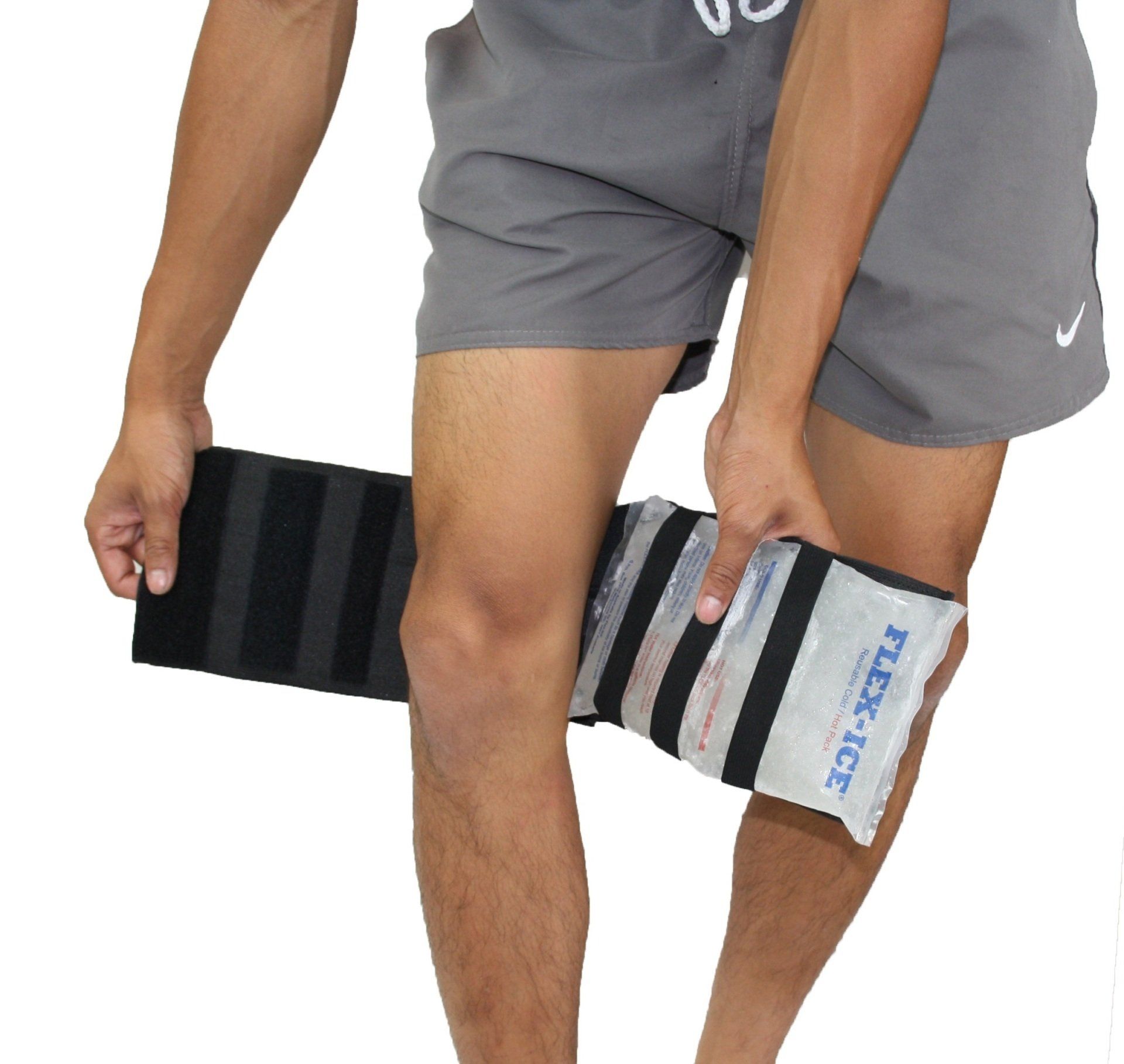
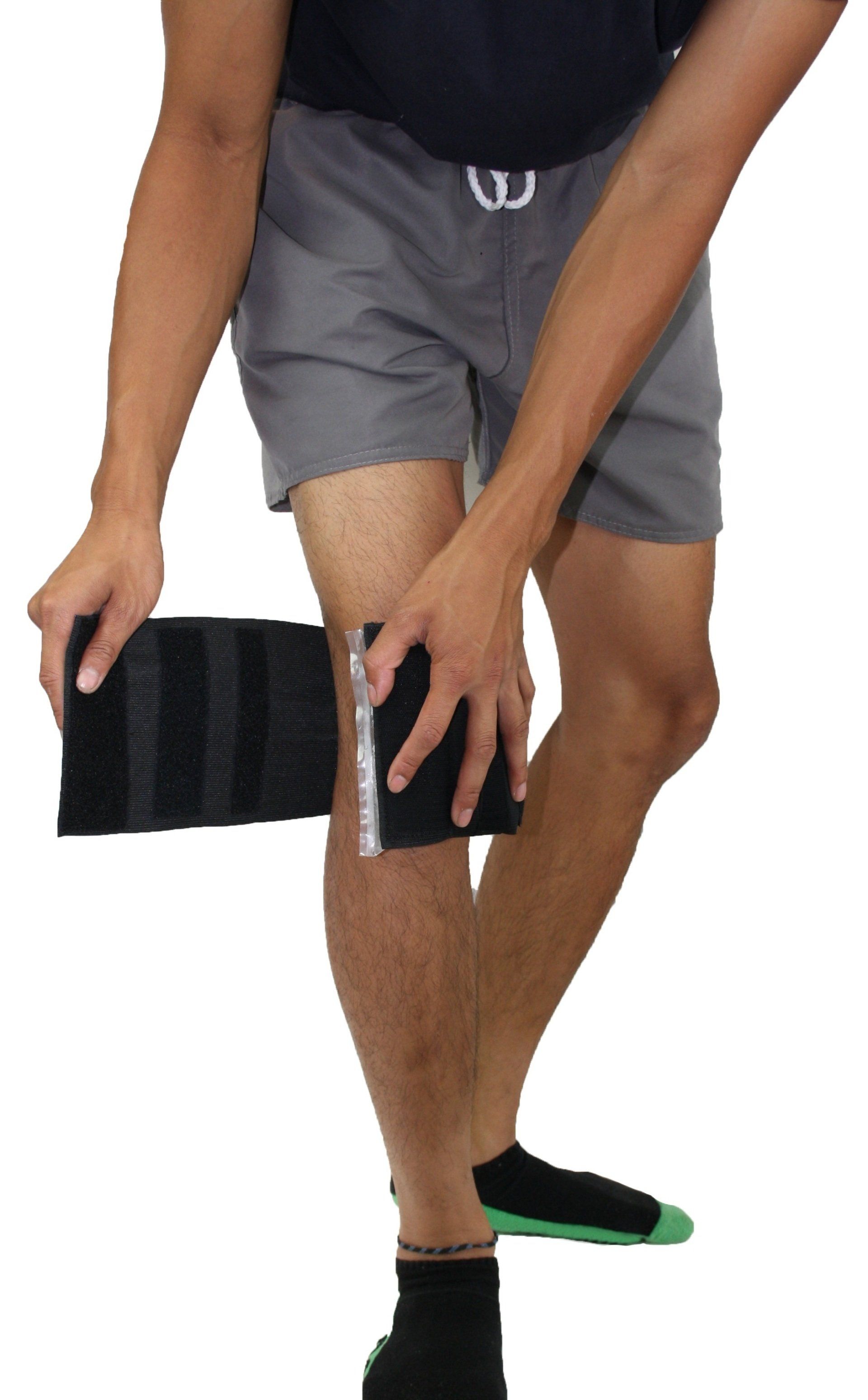
How to apply Flex-Strap
Simply insert a previously cooled or heated Flex-Ice gel pack under the stretchable elastic bands.

Note: Flex-Strap can deliver Hospital Strength Compression.
Stretch 20-50cm to your desired level of compression. Cold or Heat Therapy applied with Strong Compression is a powerful modality and should always be applied with care.
How to cool the Flex-Ice pack
Store the Flex-Ice pack flat in the freezer ready for immediate use. When the pack is cooled the clear gel inside forms ‘flex-ice’ a soft white paste ready to deliver a recommended treatment.
How to heat the Flex-Ice pack
Microwave: Heat Flex-Ice for 1 minute on high.
REMEMBER - Microwave power will vary and affect the time required to reach your desired temperature. Also the temperature of the pack before microwaving is to be considered.
After one minute remove the pack and massage the pack a little to distribute the heat evenly (temperature will continue to rise slightly). Carefully check desired temperature by holding Flex-Ice against the inside forearm. If further heating is required heat at 10-20 second intervals until you reach your desired temperature (note total time for future reference). If heating the pack directly from the freezer remove all attached ice (best to just run under warm water until ice is gone) and dry before heating. Heat Flex-Ice for 2 minutes on high then at 20 second intervals until you reach your desired temperature.
Hot Water: Heat approx. 2 litres of water. Pour the water into a suitable container. Place Flex-Ice in the hot water for approx. 120 seconds. If the pack is not hot enough place back in hot water for a further 30 seconds. If removing Flex-Ice from the freezer initially place Flex-Ice in hot water for approx. 5-7 min
FAQ
Please note tips and advice provided on this website are not a substitute for medical advice.
Always consult your surgeon or healthcare provider.
Every individual person’s injury is unique and conditions treated with Hot or Cold Therapy vary widely.
If you suspect that you may have a health problem always consult a Doctor and follow medical advice regardless of the information on this website.
Does it matter whether I use hot or cold therapy?
Yes. Knowing when to use Hot or Cold therapy is important. If you apply a heat to the wrong type of injury (an acute injury) it can potentially worsen the condition and prolong your recovery time.
Cold Therapy should be used in acute situations.
Redness, swelling, pain & inflammation are signs of an acute injury. So if you have a recent injury (within the last 48 hours) you should be applying cold therapy with compression.
Cold Therapy if you have bumps or bruises, pulled muscles, joint sprains and fractures.
Cold Therapy if you are recovering from a surgical procedure.
Cold Therapy when you have just finished playing sport or strenuous activities
Note: When applying any cold product that is below freezing an insulation layer should be used to guard against frost bite.
Heat Therapy should be used for chronic conditions.
Chronic conditions gradually build up over several days, weeks, even years.
A condition will begin to become chronic after 6 weeks.
Heat therapy will help period cramps, arthritic pain or muscle cramps/spasm.
Note: Heat Therapy should only be applied when all swelling has been reduced.
Cold / Heat Therapy
COLD PRECAUTIONS
Do not use on infants. Young children should be supervised whilst using this product. Elderly or disabled persons may also require supervision. Any cold product may cause frostbite if improperly used. Do not use Cold Therapy before sporting activities as it can lower the area’s proprioception. People with circulatory disorders should not use cold therapy.
HOT PRECAUTIONS
Never apply heat to bruises or muscle strains in the first 24 hours. Heat may increase any local bleeding. Persons with diabetes, circulatory problems, nerve damage, paralysis or sensitive skin should not use heat therapy except if directed by a health practitioner. When pregnant do not apply heat to the abdomen. Do not apply heat therapy where a clot or thrombosis is suspected.
Contrast Therapy
Compression Therapy
Why is Compression Important?
Compression is required after injury to prevent oedema formation (swelling). Think how effective pressing on a cut finger is when you have a bleeding finger? This is why you should apply compression as fast as possible if you have a twisted ankle for example. You need to compress the injured area to stop excessive internal bleeding (when blood becomes trapped under the skin).It is important to stop blood flowing and pooling around the injured area. Too much swelling results in the death of healthy cells in the area (dying due to a lack of oxygen.) This can cause significant loss of function, increased recovery time, excessive pain and is more likely to lead to a long term injury. Compression will greatly increase the transfer of heat or cold. Think about the difference of touching something hot or cold as opposed to strongly grabbing an object that is hot or cold.
Post Op Information
It is common after surgery to have swelling especially in the lower extremities. After surgery such as a knee replacement swelling should be expected so it is important to apply compression and cold therapy to help stop the inflammation. It is difficult to give advice on post-surgical applications as every condition is different. Swelling can persist for months but generally after a knee operation swelling is greatly reduced by 6-8 weeks. Please consult your healthcare provider. Some swelling can last for months.
When applying Cryotherapy you want it to be not only effective but as easy to apply as possible as multiple applications will usually be required. After time (consult your doctor) exercise is important for blood circulation as the pumping effect helps flush out toxins while strengthening the muscles and ligaments in the area. However the exercise should be low impact and for short periods (start slow and consult your doctor)
If you have been recommended / used Flex-Ice in your hospital you may need to purchase direct from us. Consult with your surgeon if you are unsure.
Sprains and Strains
What happens when I get injured?
Typical joint injuries occur in the knees, ankles, shoulders, elbows and wrists. Injuries can cause joints to swell and suffer from excessive inflammation. When you have an injury or trauma such as a twisted ankle. Your body reacts by flooding the affected area with plasma and red blood cells in an attempt to neutralize the threat. This is called the inflammatory process an innate primitive defence mechanism that gets activated whenever the body feels under attack. The vessels that supply blood to our muscles and other parts of the body are muscular and are able to contract (vasoconstriction) and expand (vasodilation) increasing and decreasing the diameter of the blood vessels. Ultimately what happens is that there is a vasodilatory response so more blood rushes in and the wall of the blood vessels leak fluids into the surrounding area. (this is the swelling you see in a twisted ankle) Inflammation is an important part of the healing process however too much inflammation can cause excessive swelling with fluids rushing in and cutting off nearby healthy cells from getting the oxygen they need to function and stay alive. This increases the damaged area, decreases the strength of repair and lengthens recovery time.
Inflammation
Sports Trainers / Post Game Recovery
Flex-Strap (Flex-Ice Compression Strap applied with a Flex-Ice gel pack)can professionally treat acute injuries extremely well.
Flex-Strap designed to cool and compress like no other product.
Strong Compression / Innovative Design
Applying compression is important for sports injuries and it should be applied as soon as possible.
A combination of strong elastic and sticky hook and loop strips deliver strong comfortable compression. Flex-Ice Compression is designed to match an average person’s upper body strength. Designed so one person is capable of stretching the Flex-Strap effectively to provide strong enough compression when required. When applying to larger areas application needs to be done in 2 separate actions to ensure effective application over the entire treatment area. Think of the Flex-Ice Compression Strap like a large Band-Aid that stretches and sticks together.
Flex-Ice Compression Strap can apply any cooling or heating device to the body. If a cold Flex-Ice gel pack isn’t available you can use the Flex-Strap to apply a bag of ice or an ice bag. The compression delivered will easily compress any device to the body. Elastic that will stretch and compress many times more than neoprene. Flex-Strap is made of quality materials – and it really packs a punch because if it’s not stretching it’s sticking!
Flex-Strap will provide professional icing quickly and easily for the whole team. In a highly acute situations extreme compression can be delivered by applying multiple Flex-Straps. Please note when Flex-Straps are tightly wrapped on top or around each other the amount of compression applied will be very significant.
Please test on yourself before placing on a patient.
Unlike other products on the market all the compression is delivered through the gel pack as the FlexStrap is designed to compress down on top of the gel pack. This design also allows the gel packs to be placed side by side for complete coverage (and compression) when treating larger areas. Flex-Ice gel packs have no side edges so they fits snuggly next to each other.
Flex-Ice Compression Strap is compact and will easily fit in your back pocket. Enough for a whole team in a shoe box. Designed to last with over 25 separate independent stitching areas. This one universal design not only does what a bag full of other hot and cold products will do – it will do it better!
Sticky Flex-Ice club room wall board available for convenient storage and easy access.